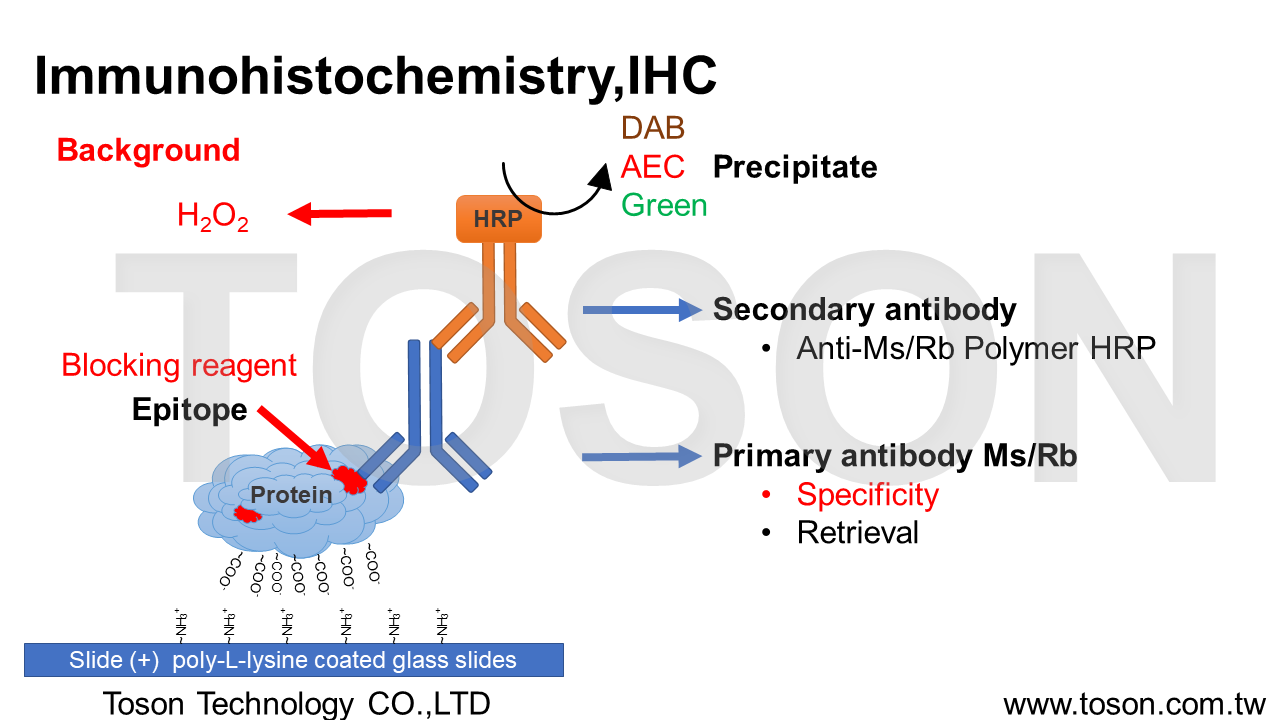
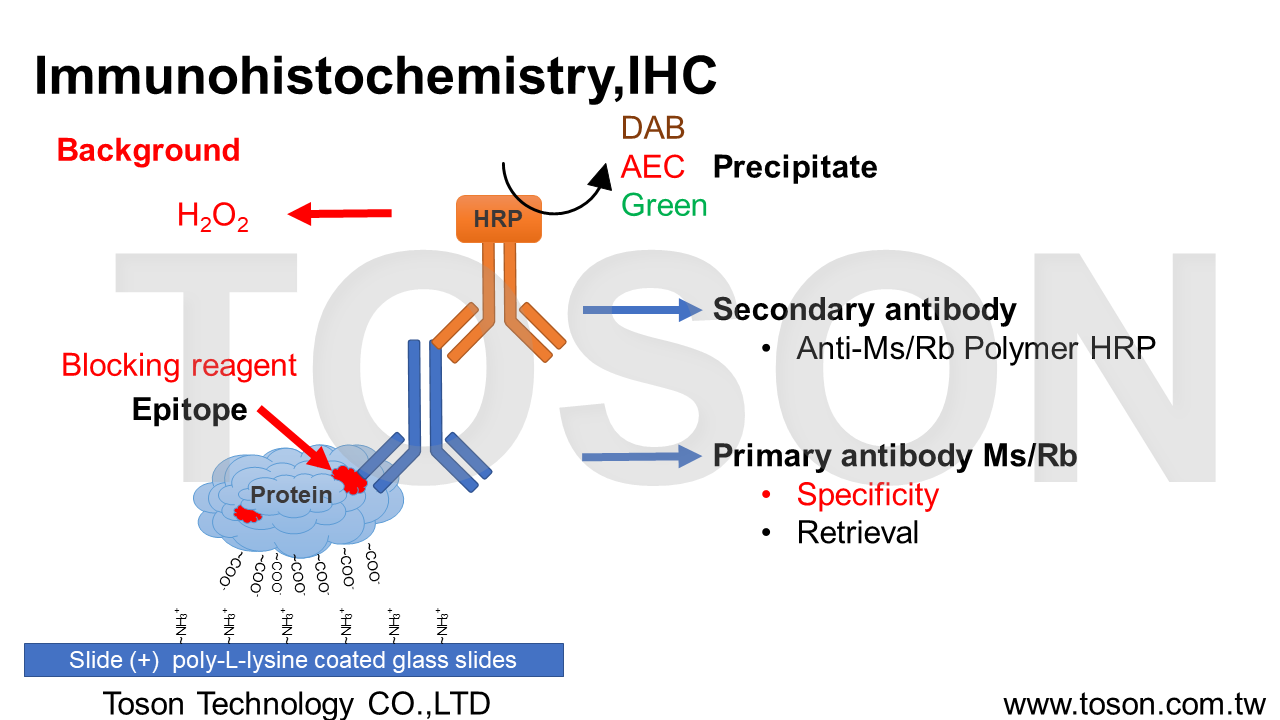
Immunohistochemistry staining Kit , IHC ( for Protein )免疫病理化學染色 ( 針對蛋白質 )
Immunohistochemistry , IHC為具有專一性之呈色,藉由組織上蛋白質的抗原表位Epitope與抗體Antibody進行非共價鍵結合Non-covalent bonding (ex:凡德瓦爾利Van der Waals forces、氫鍵hydrogen bonds、靜電作用electrostatic interactions),以偵測組織或細胞內目標蛋白質的表現量及位置。
(一)、固定與切片 Fixation & Section組織切片前多以10% 福馬林固定Formalin fixation維持蛋白質型態,切片後會貼於有poly-L-lysine塗層之玻片上烤片,使組織固定在玻片上。
(二)、過氧化氫處理 Hydrogen peroxide組織內含有超氧化物歧酶Superoxide Dismutase ,SOD,尤其腦、肝、血液等含量特別高,因此若使用可見光呈色劑Chromogen作呈色時(DAB、AEC、HRP Green),需經過3% H2O2處理,使SOD破壞,減少Polymer HRP呈色的背景Background。
(三)、抗原修復 Retrieval福馬林固定石蠟包埋Formalin Fixation Paraffin Embedded ,FFPE中,由於甲醛的化學特性,能使不帶電荷的氨基酸間以亞甲基橋Methylene bridge(-CH2-)的方式形成交聯Cross-links。(Lys, Tyr, Trp, Cys, His, Arg, Asn, Gln)但Cross-links會導致肽Peptides及Epitopes的抗原性Antigenicity降低,因此透過抗原修復Retrieval來回復與Antibody bidding的能力。
(四)、阻斷劑 Blocking組織切片經過適當的Retrieval後,為了減少抗體對於組織的非專一性結合non-specific bidding產生,會使用BioTnA特別對於IHC優化的非血清性Non-rerum Immunoblocking reagent,可有效降低背景Background的產生。
(五)、抗體結合與沉澱 Antibody bidding & Precipitate組織切片經過適當的Retrieval後,使Methylene bridge打斷,便可使一級抗體Primary antibody與Epitope達到良好的bidding,主要利用抗體上的抗原結合區段Fragment antigen binding ,Fab可以有效的辨識Antigen上的Epitope進行專一性結合。隨後以二級抗體Secondary antibody(Polymer HRP)來連接Primary antibody的抗原結晶區Fragment crystallizable region ,Fc端,因具有辣根過氧化物酶Horseradish Peroxidase,可使Chromogen氧化後沉澱Precipitate,將被bidding的Epitopes呈陽性反應Positive。
二、染色目標與應用:
由於IHC涉及特異性抗原-抗體反應,與僅能以有限的蛋白質、酵素和組織結構進行識別的 傳統特殊酶染色技術相比,IHC具有明顯的優勢。因此IHC已成為一項至關重要的技術, 並已在許多醫學研究實驗室以及臨床診斷中廣泛使用,如癌症的預後標記Prognostic Markers in Cancer、組織內未知腫瘤Tumors of Uncertain Histogenesis、發育與凋亡Development and Apoptosis、神經性退化疾病Neurodegenerative Disorders、腦外傷Brain Trauma、 肌肉中疾病Muscle Diseases 等etc,IHC可見光染色可分為單色染色Single stain、雙色染色Double stain、三色染色Triple stain 三種染色方法,其染色原理均相似,主要取決為預觀察之目標及期望的表現形式,透過Antibodybidding的位置以及使用的Chromogen來呈現其結果, 下列表格將簡單整理BioTnA各式染色之Kit組、bidding的位置以及使用的Chromogen來呈現其結果,
下列表格將簡單整理BioTnA各式染色之Kit組。

►細胞核Nucleus-藍色Hematoxylin 或 紅色 Fast Red
►陽性反應Positive-棕色DAB、紅色AEC、綠色HRP Green 或藍色Alk Blue
四、Immunohistochemistry,IHC 實際染色參考:
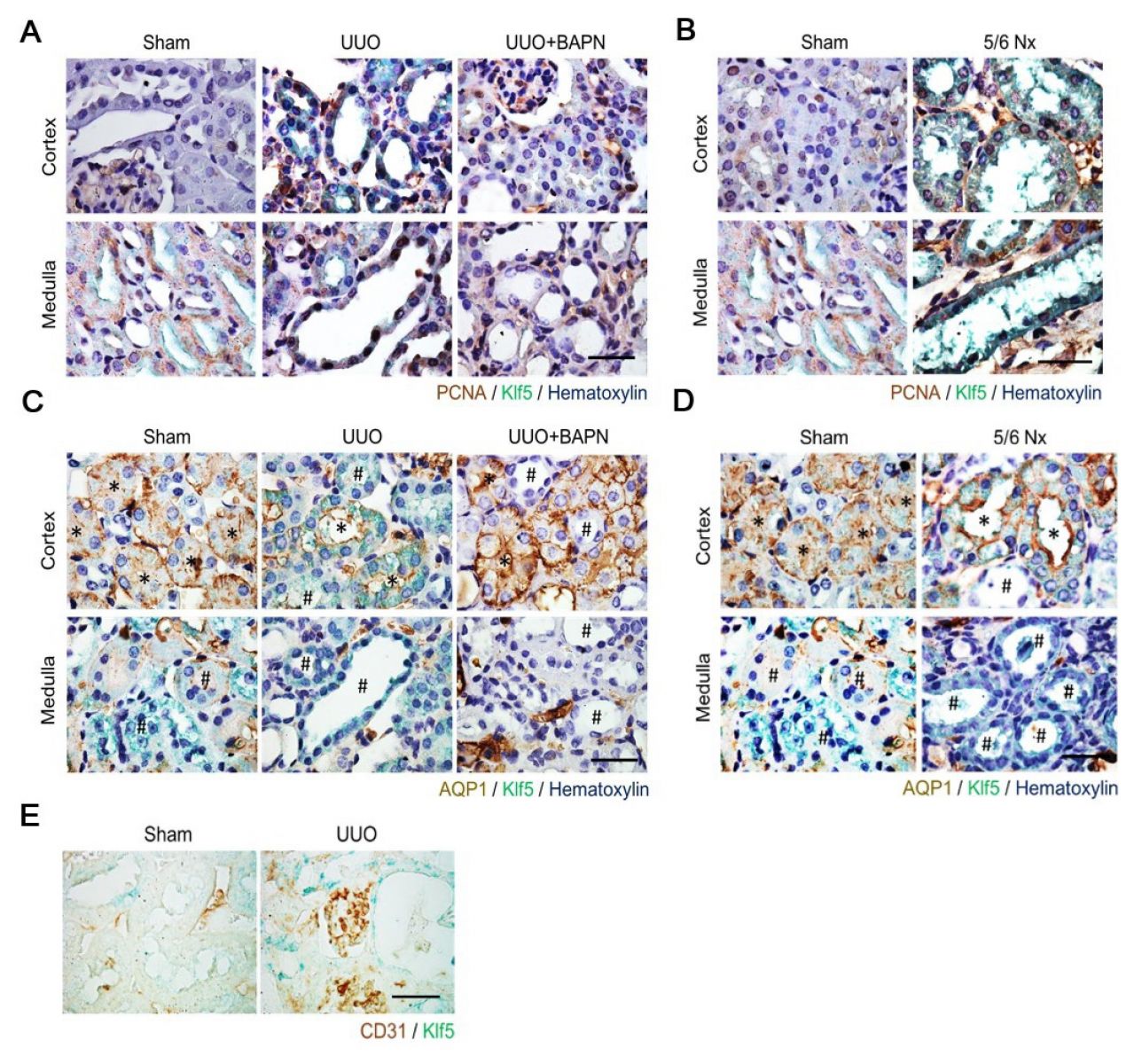
Attachments Figure A
Stiff matrix–up-regulated Klf5 accompanied with cell proliferation mainly occurs in renal tubular cells
but not in renal endothelial cells or fibroblasts.
►A and B: Representative images show IHC double staining with anti-Klf5 (green) and anti-PCNA
(brown, a marker of cell proliferation) antibodies of kidney sections from sham (operated control),
UUO, or UUO + BAPN .
►C and D: Representative images show IHC double staining with anti-Klf5 (green) and anti-AQP1
[brown, a marker of PT (asterisks)] antibodies of kidney sections from Sham (operated control),
UUO, or UUO + BAPN.
►E: Representative images show IHC double staining with anti-Klf5 (green) and CD31(brown,
a marker of endothelium) of kidney sections from sham and UUO mice.
五、Immunohistochemistry staining Kit 染色步驟(Protocol)

BioTnA Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Single stain kit
►Water Extract and Its Bioactive Components Ameliorate Dermal Damage in UVB-Irradiated Skin Models
BioTnA Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Double stain Kit
►Matrix-StiffnesseRegulated Inverse Expression of Kruppel-Like Factor 5 and Kruppel-Like Factor 4 in the Pathogenesis of Renal Fibrosis Attachments: A B C D
►Expression of Helios in gastric tumor cells predicts better survival in gastric cancer patients